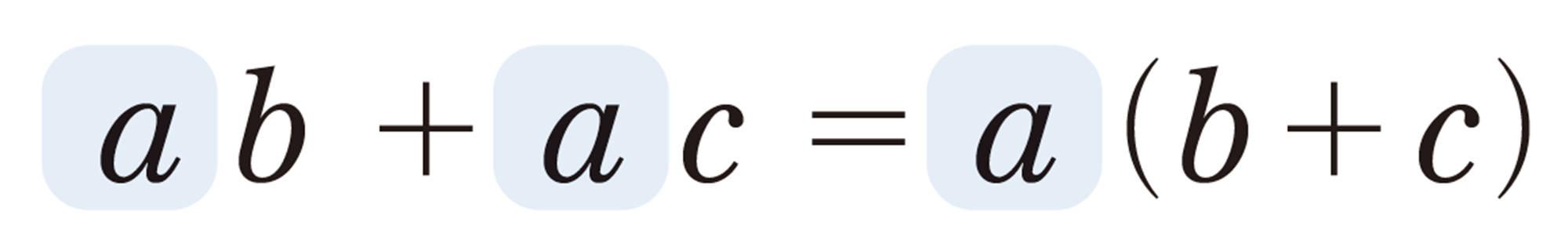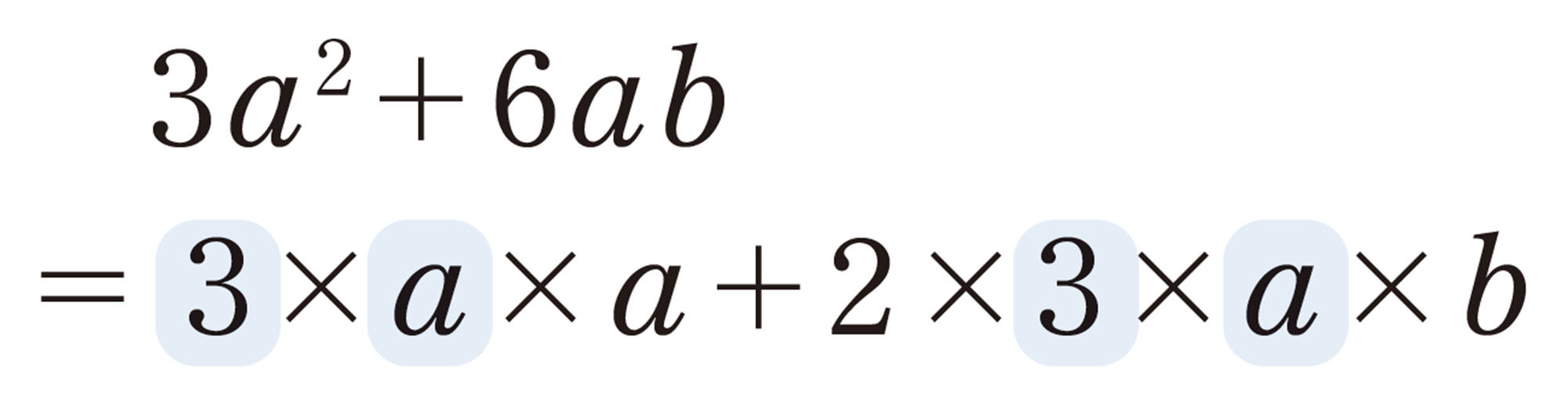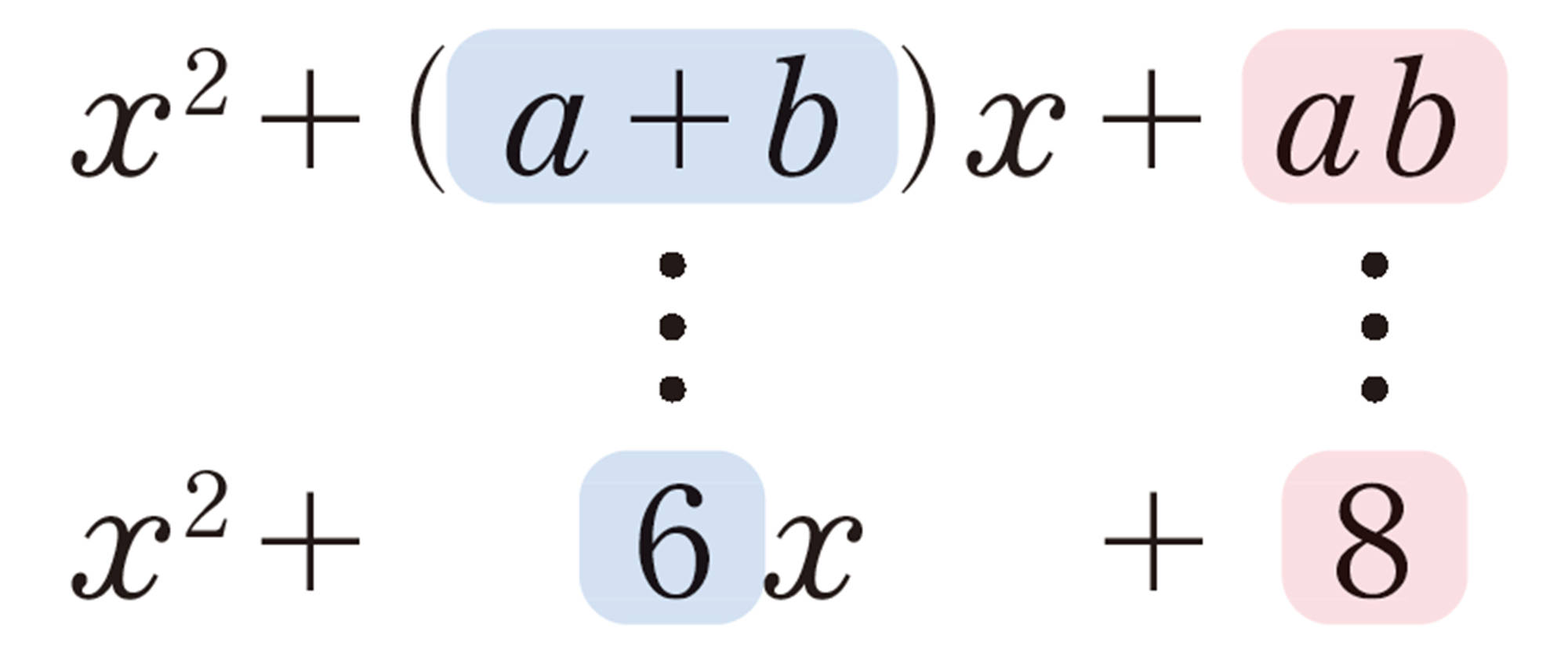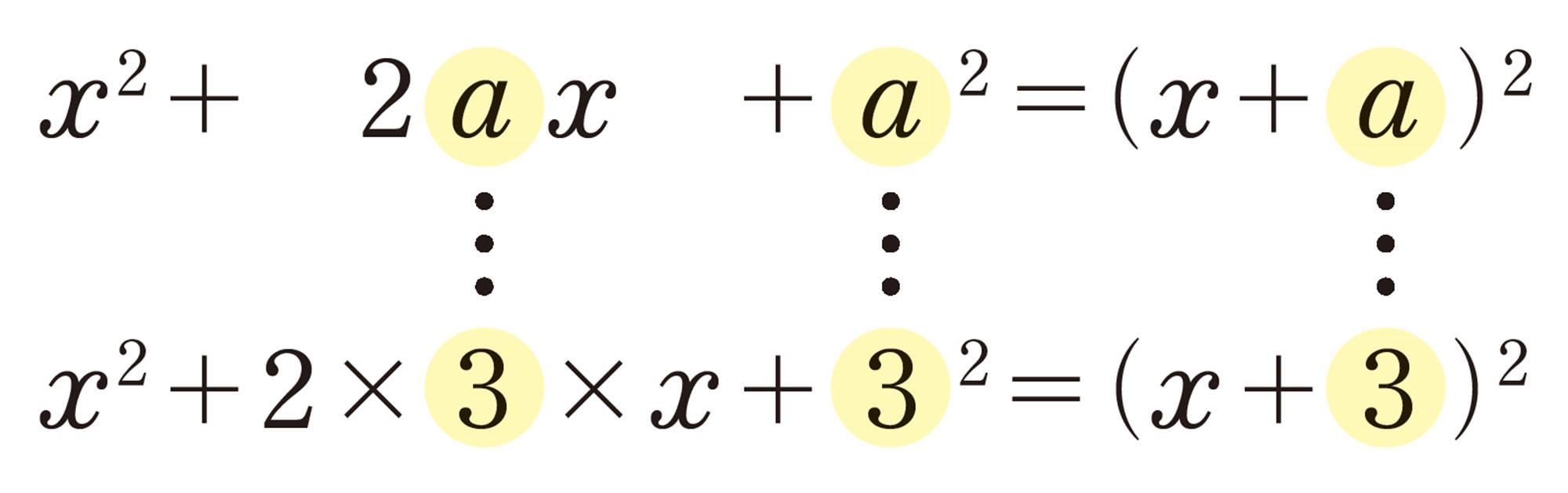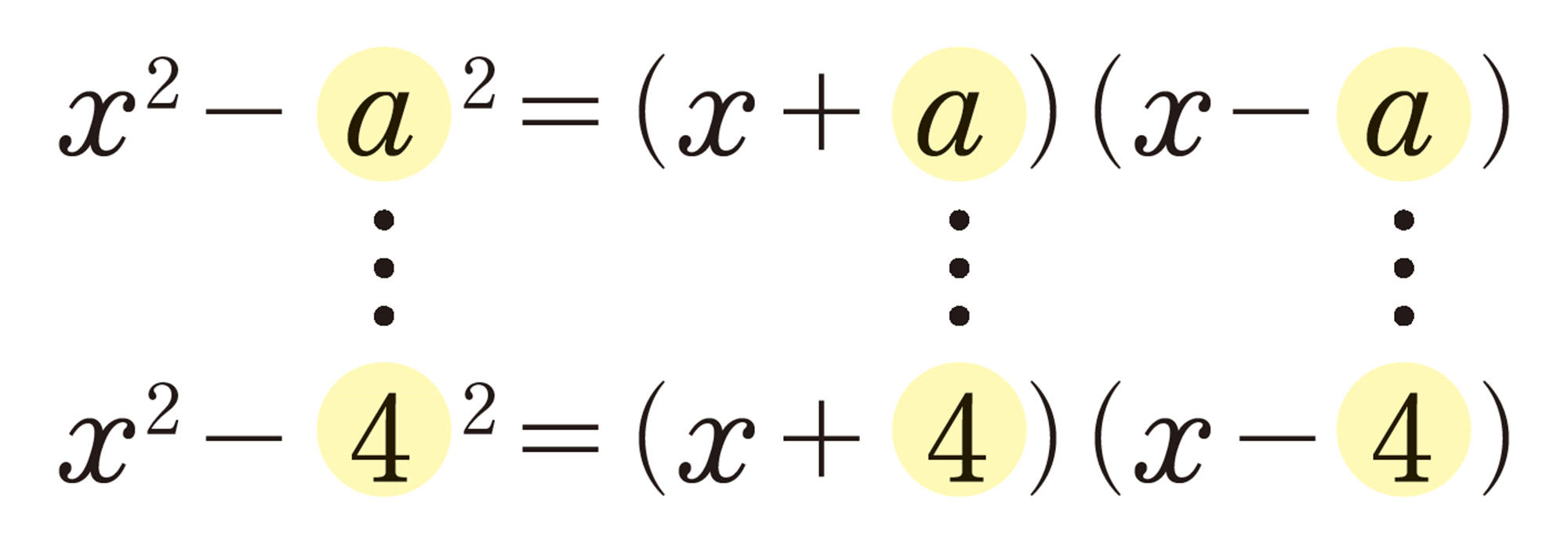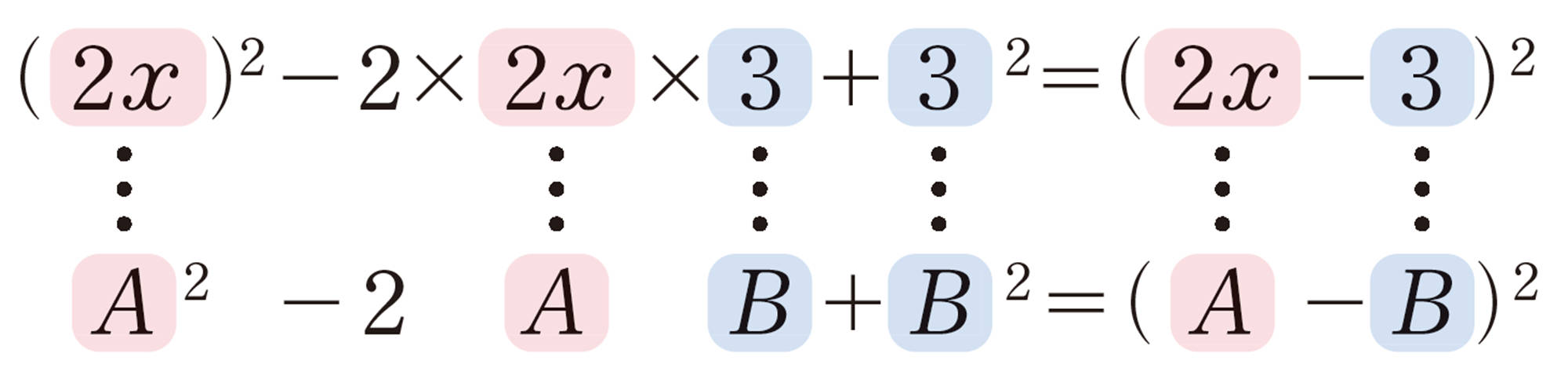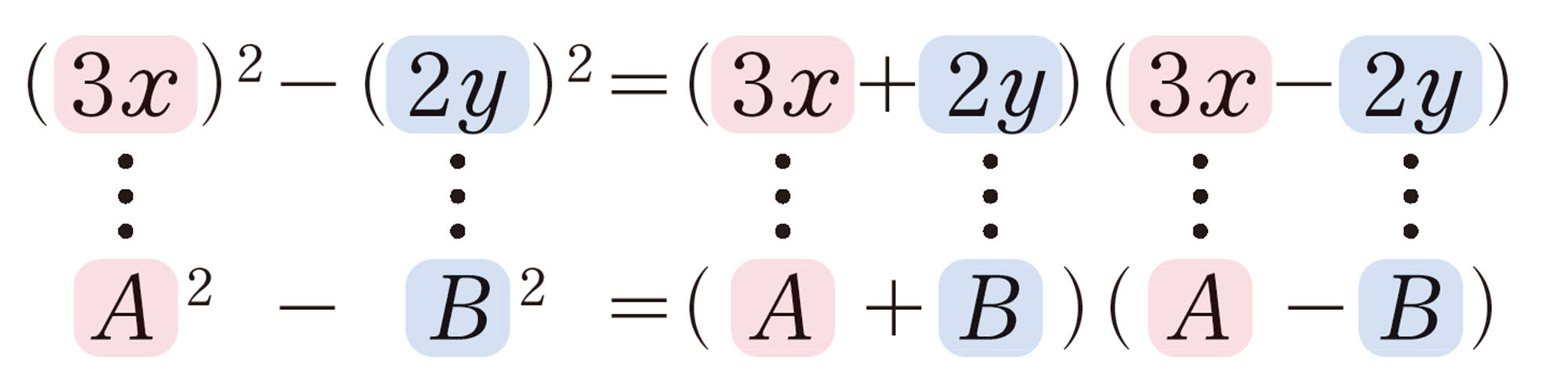<3年p.23>
2節 因数分解
長方形の面積は?
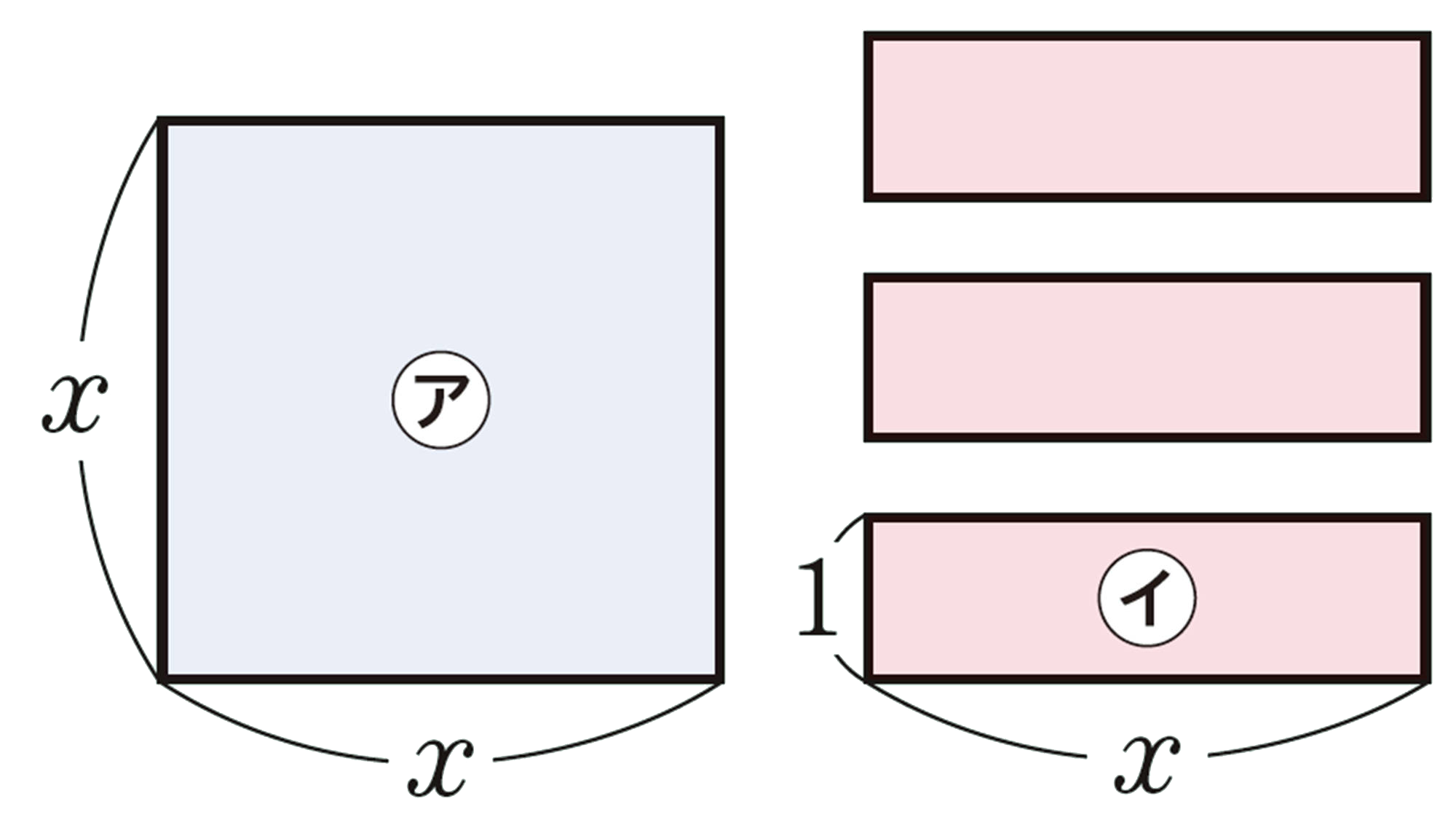
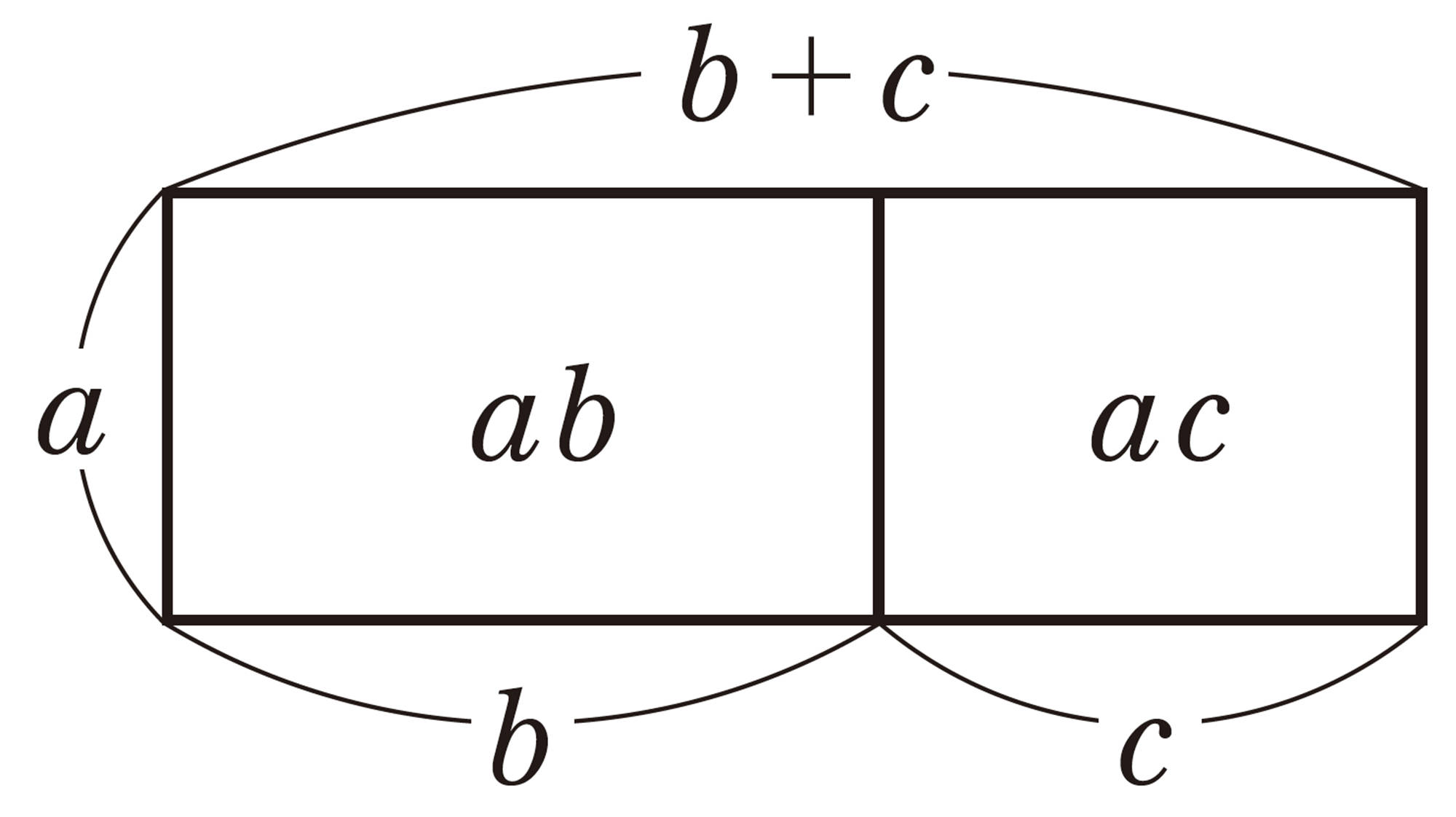
長方形や正方形の紙を並べかえて,1つの長方形をつくってみましょう。
巻末③の図を切り取って使いましょう。
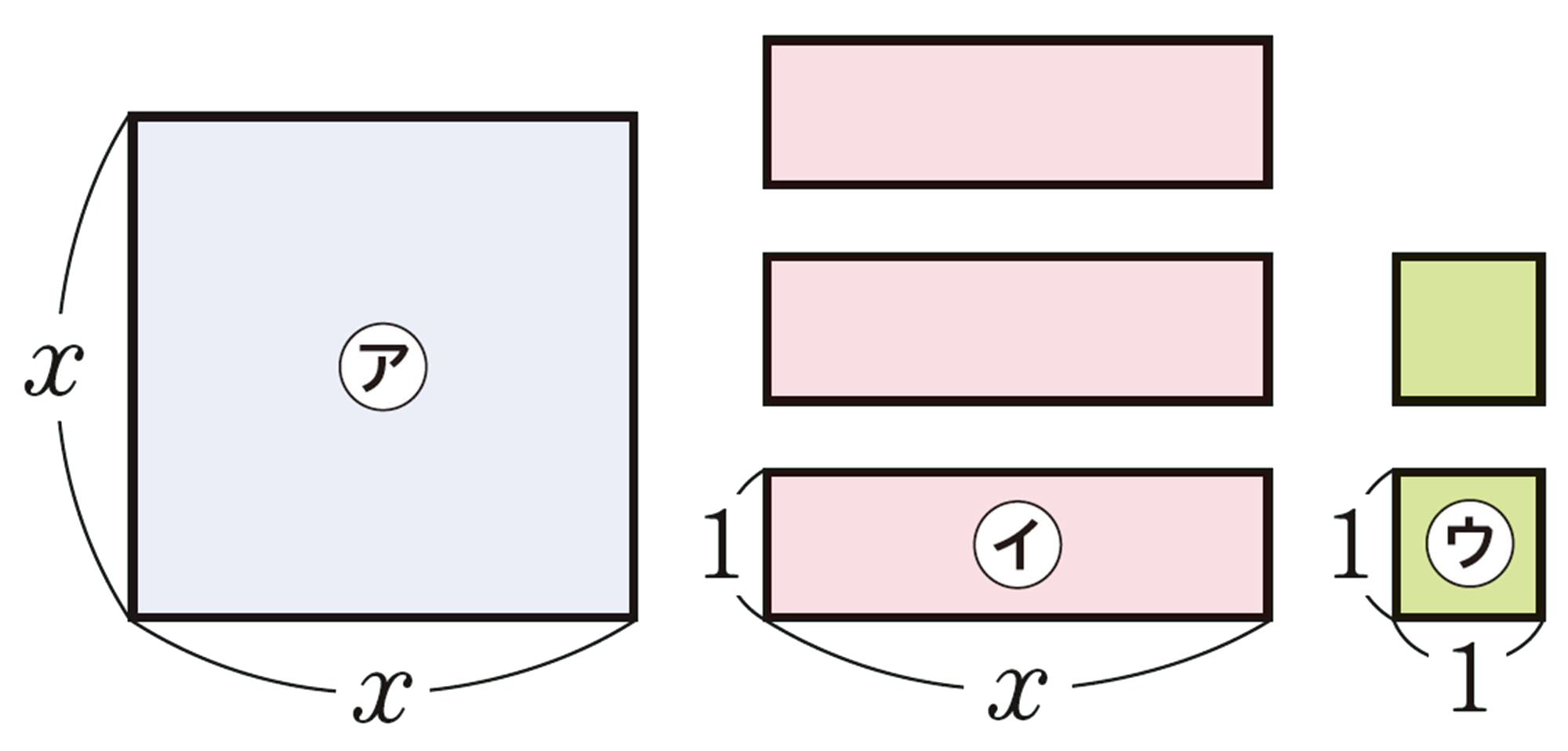
【1】 右の正方形や長方形の紙を並べかえて,1つの長方形をつくりましょう。
㋐を1枚,㋑を4枚,㋒を3枚使って,つくってみよう。


㋐,㋑,㋒がそれぞれどんな枚数でも,長方形がつくれるのかな。
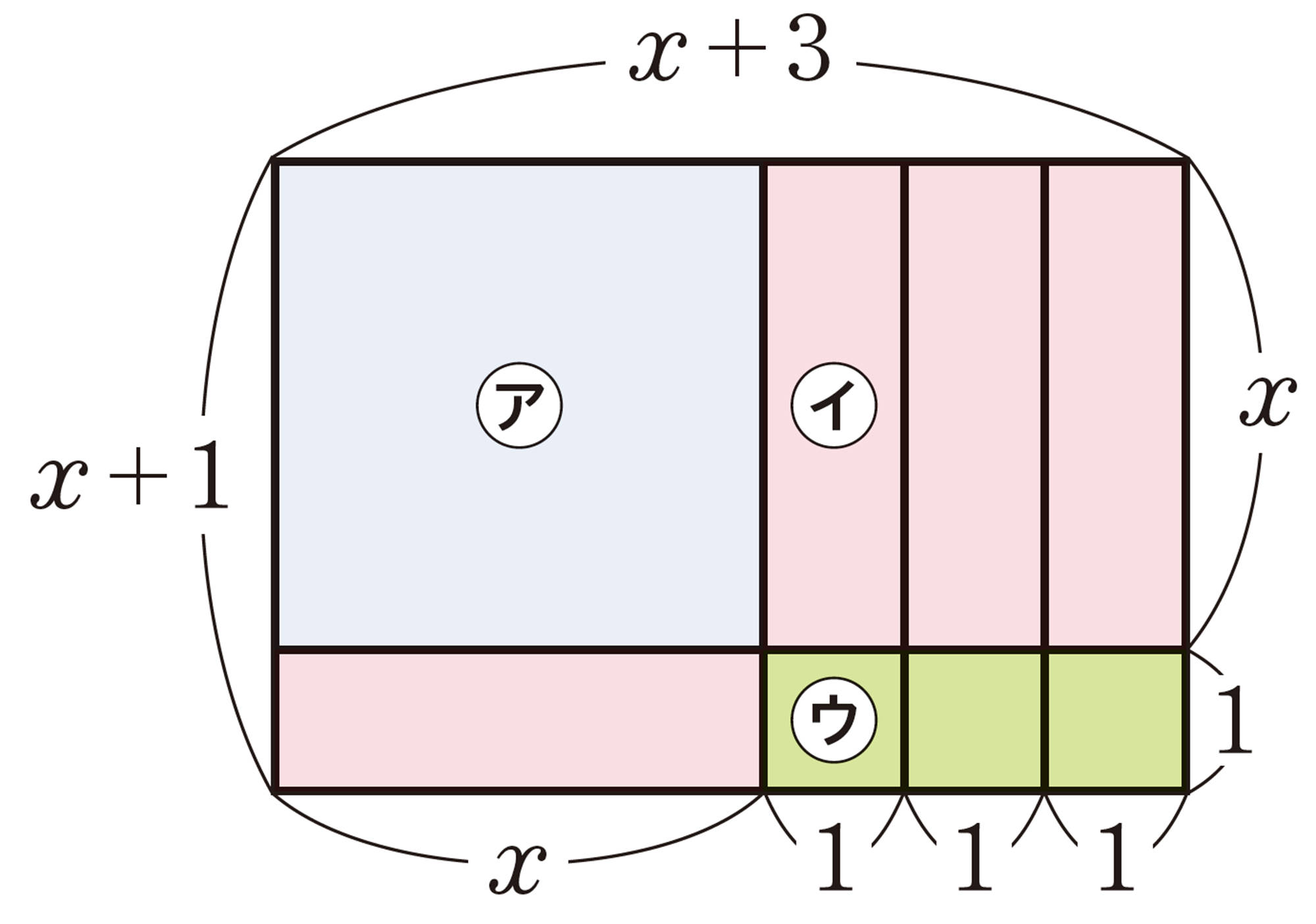
【2】 ⑴〜⑶でつくったそれぞれの長方形について,面積を式で表し,気づいたことを話し合いましょう。
並ベかえる前の正方形や長方形の面積の和と,並ベかえてできた長方形の面積の2つの式で表せるね。


式は,単項式の和の形と単項式や多項式の積の形の2つできるということだね。
次の課題へ!
展開された式を,単項式や多項式の積の形に表すことができるのかな?
P.24

<3年p.24>
1 因数分解
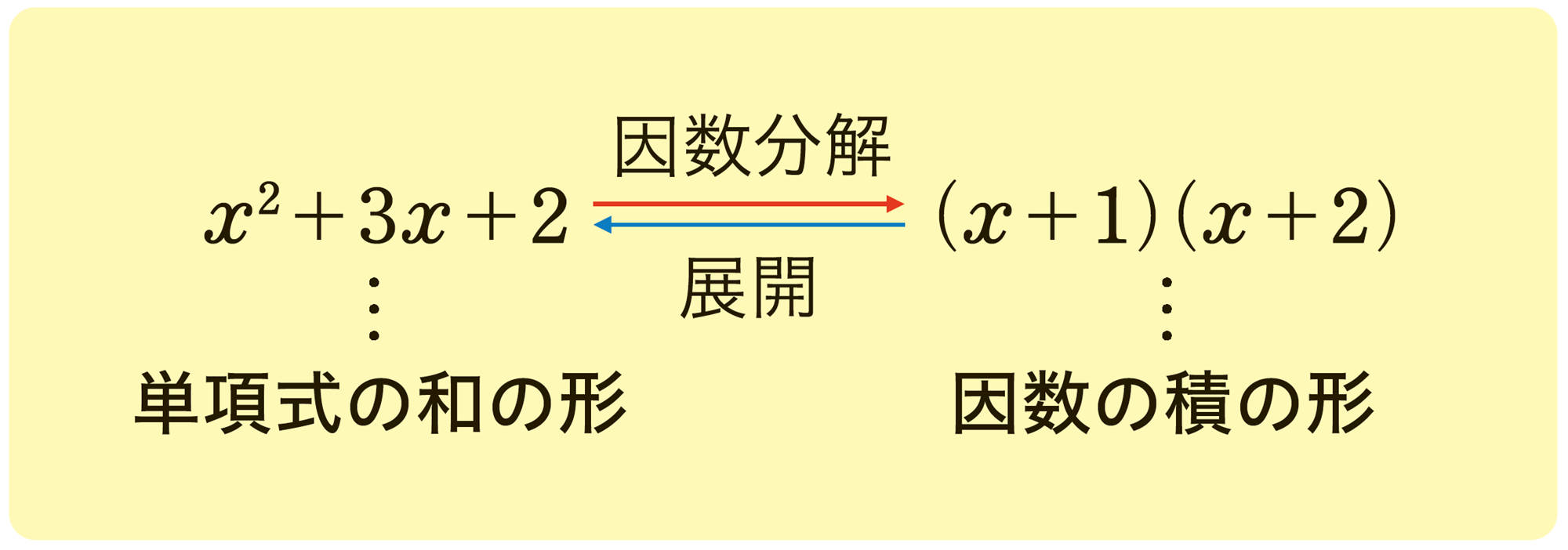
多項式の中には,いくつかの式の積の形で表すことができるものがある。たとえば,前ページの【1】 ⑴,⑵から,次の式が成り立つことがわかる。
① [mathjax]\(x²+3x=x(x+3)\)
② [mathjax]\(x²+3x+2=(x+1)(x+2)\)
このように,多項式をいくつかの単項式や多項式の積の形で表すとき,一つひとつの式をもとの多項式の因数という。
たとえば,①のx,[mathjax]\(x+3\)は,多項式[mathjax]\(x²+3x\)の因数であり,②の[mathjax]\(x+1\),[mathjax]\(x+2\)は,多項式[mathjax]\(x²+3x+2\)の因数である。
[mathjax]\(30 = 3 \times 10\)と表すとき,3と10はそれぞれ30の因数というよ。

ふりかえり
目標 ▷ 多項式を,いくつかの式の積の形に表す方法を考えよう。
多項式をいくつかの因数の積の形で表すことを,その多項式を因数分解するという。
問 1 次の㋐〜㋓の式のうち,因数分解をしているものはどれですか。
㋐ [mathjax]\(x²-5x=x(x-5)\)
㋑ [mathjax]\(x²+7x+12=x(x+7)+12\)
㋒ [mathjax]\(x²+6x+8=(x+3)²-1\)
㋓ [mathjax]\(x²-9=(x+3)(x-3)\)
<3年p.25>
共通な因数
例 2
⑴
⑵
問 2 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(ax + bx\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(ax – a\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(px² – 5px + 3p\)
例 3 多項式[mathjax]\(3a² + 6ab\)を因数分解しなさい。
解答
答 [mathjax] \(3a(a+2b)\)
注意 [mathjax]\(3a²+6ab\)を因数分解するときには,[mathjax]\(3(a²+2ab)\)や [mathjax]\(a(3a+6b)\)などのままにせず,共通な因数は残らずかっこの外にくくり出す。
問 3 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(4ax+8ay\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(3x²+7x\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x²-x\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x²y+xy²\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(a²+6ab-8a\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(9x²-3xy+6x\)
やってみよう
計算力を高めよう2-1
P.31
どんなことがわかったかな
共通な因数がある多項式は,因数分解することができます。
次の課題へ!
因数分解は展開の逆になっているから,乗法公式の逆の考え方で因数分解できるかな?
P.26

<3年p.26>
2 公式による因数分解
目標 ▷ 乗法公式を利用して,多項式の因数分解を考えよう。
[mathjax] \(❶´\) [mathjax]\(x² + (a + b)x + ab = (x + a)(x + b)\)の公式
解答
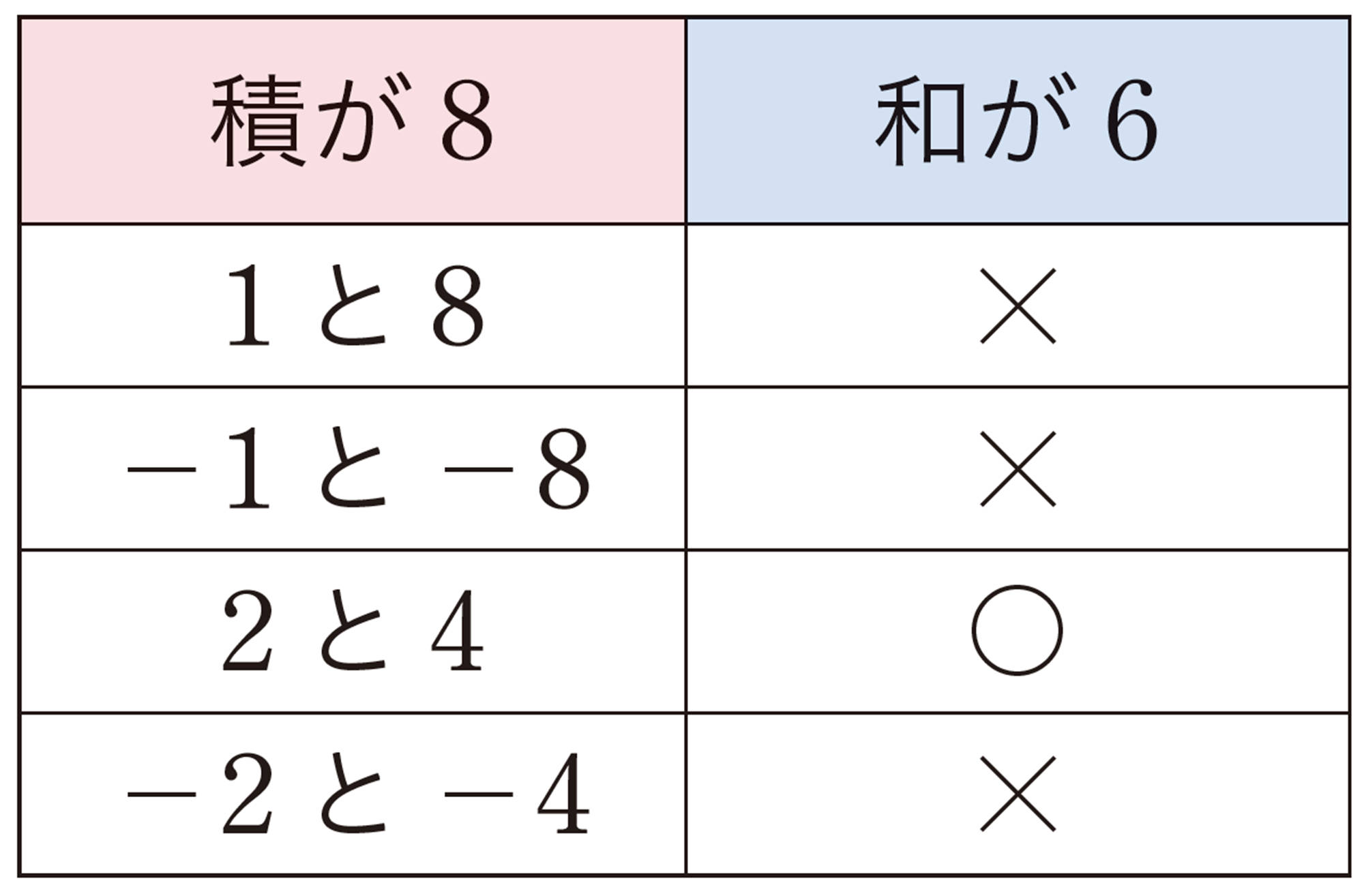
答 [mathjax] \((x+2)( x+4)\)
なぜ,先に積が8になる2数を考えるのかな。

注意 答えは,[mathjax]\((x + 2)(x + 4)\),[mathjax]\((x + 4)(x + 2)\)のどちらでもよい。
問 1 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(x² + 5x + 6\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(x² + 9x + 8\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x² – 7x + 10\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x² – 5x + 4\)
問 2 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
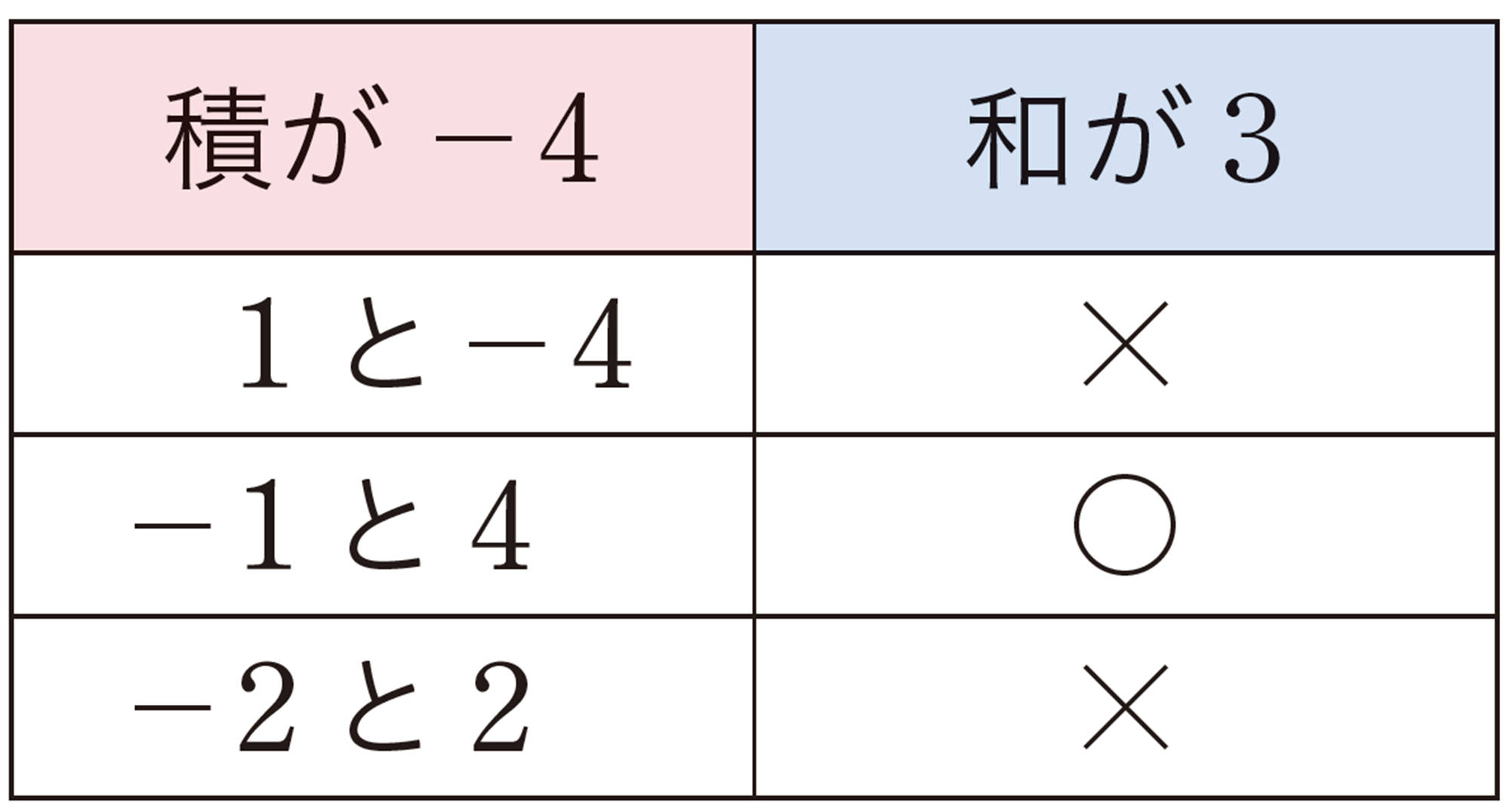
⑴ [mathjax]\(x²+x-12\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(x²+2x-3\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x²- 2x-15\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x²-4x-5\)
<3年p.27>
[mathjax] \(❷´\) [mathjax]\(x² + 2ax + a² = (x+a)²\),[mathjax] \(❸´\) [mathjax]\(x² - 2ax + a² = (x-a)²\)の公式
解答
答 [mathjax] \(( x+3)² \)
問 3 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(x² + 2x + 1\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(x² – 2x + 1\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x² + 4x + 4\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x² – 8x + 16\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(a² + 12a + 36\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(y²- 14y + 49\)
[mathjax] \(❹´\) [mathjax]\(x² - a²=(x + a)(x - a)\)の公式
問 4 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(x² – 25\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(x² – 36\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(1 – y²\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(a² – b²\)
問 5 これまで学んだ[mathjax] \(❶´\)〜[mathjax] \(❹´\)の公式を使って,次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(x² + 8x + 12\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(x² – 4x + 4\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x² – x – 20\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x² – 100\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(x² + 18x + 81\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(x² + 3x – 28\)
やってみよう
計算力を高めよう2-2
▷P.31
<3年p.28>
因数分解の公式
[mathjax] \(❶´\) [mathjax]\(x²+(a+b)x+ab=(x+a)(x+b)\)
[mathjax] \(❷´\) [mathjax]\(x²+2ax+a²=(x+a)²\)
[mathjax] \(❸´\) [mathjax]\(x²-2ax+a²=(x-a)²\)
[mathjax] \(❹´\) [mathjax]\(x²-a²=(x+a)(x-a)\)
[mathjax] \(❷´\),[mathjax] \(❸´\),[mathjax] \(❹´\)は[mathjax] \(❶´\)の特別な場合と見ることができるね。それぞれどんな場合か説明してみよう。

いろいろな因数分解
例 5
⑴
⑵
問 6 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(4x²+4x+1\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(9x²-12x+4\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x²+2xy+y²\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x²-6xy+9y²\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(25b²-9a²\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(x²-\dfrac{y²}{4}\)
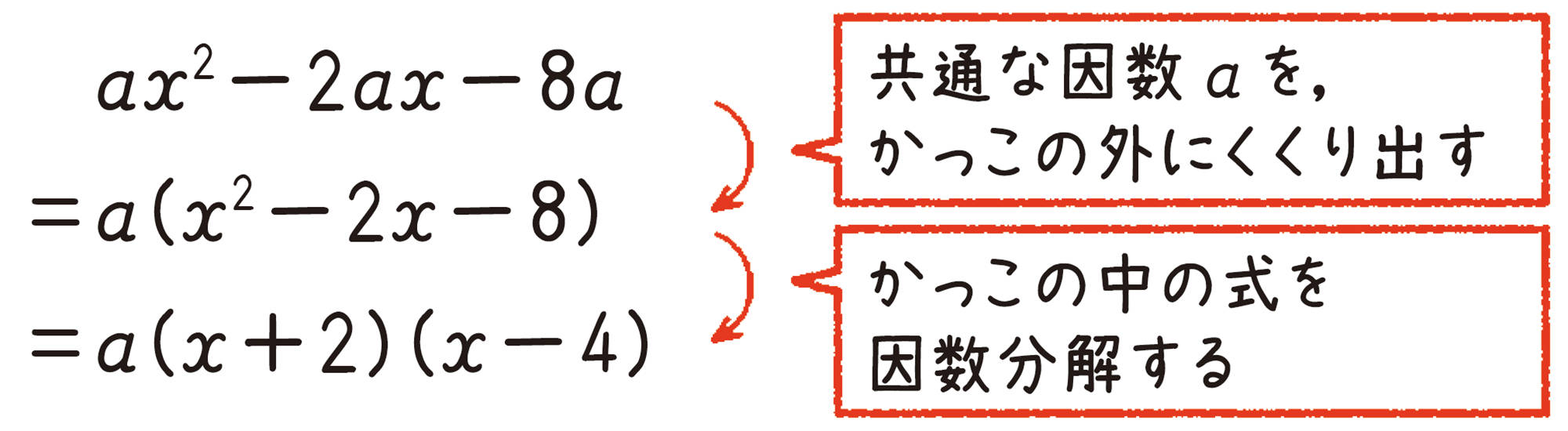
例 6 [mathjax]\(ax² – 2ax – 8a\)を因数分解しなさい。
考え方 まず,共通な因数をかっこの外にくくり出し,さらに因数分解できないか考える。
解答
問 7 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(ax²-ax-2a\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(xy²-x\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(2x²+16x+32\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(- 3x²+12xy-12y²\)
<3年p.29>
解答
例7のように,多項式を因数分解するとき,式の一部をひとまとめにして1つの文字におきかえると,分配法則や公式が使える場合がある
問 8 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\((x – 1)² – (x – 1)\)
⑵ [mathjax]\((a + b)x + (a + b)y\)
⑶ [mathjax]\((x + 7)² + 6(x + 7) – 16\)
⑷ [mathjax]\((x + y)² – 81\)
問 9 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
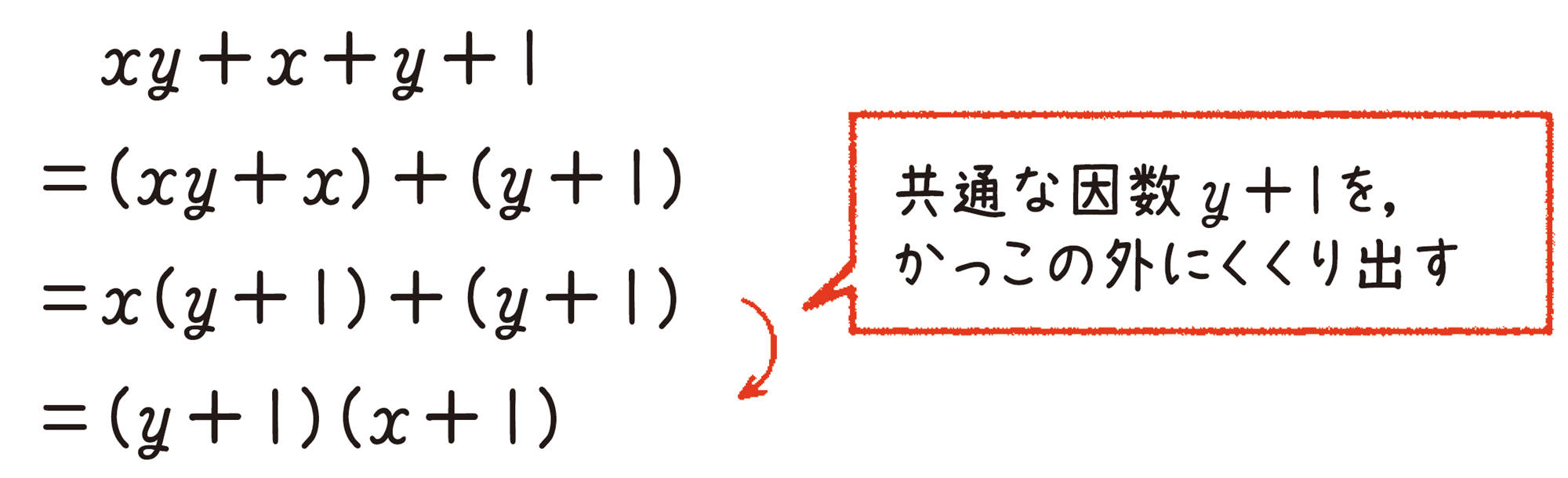
⑴ [mathjax]\(xy – x + y – 1\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(ax + 3x – a – 3\)
やってみよう
計算力を高めよう2 – 3
P.31
どんなことがわかったかな
乗法公式を使って,いろいろな多項式を因数分解することができます。
次の課題へ!
これまでに学んだ式の展開や因数分解を使って,どんなことができるのかな?
P.32

<3年p.30>
確かめよう 2節 因数分解
1 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(7ax+2ay-9a\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(12x²-8xy\)
2 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(x²+7x+6\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(x²-x-12\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x²+10x+25\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x²-16x+64\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(x²-81\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(9-a²\)
3 次の式を因数分解しなさい。
⑴ [mathjax]\(x²-4xy+4y²\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(49-9a²\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(ax²+4ax-12a\)
⑷ [mathjax]\((a+b)x-(a+b)y\)
表を使った因数分解 Tea Break
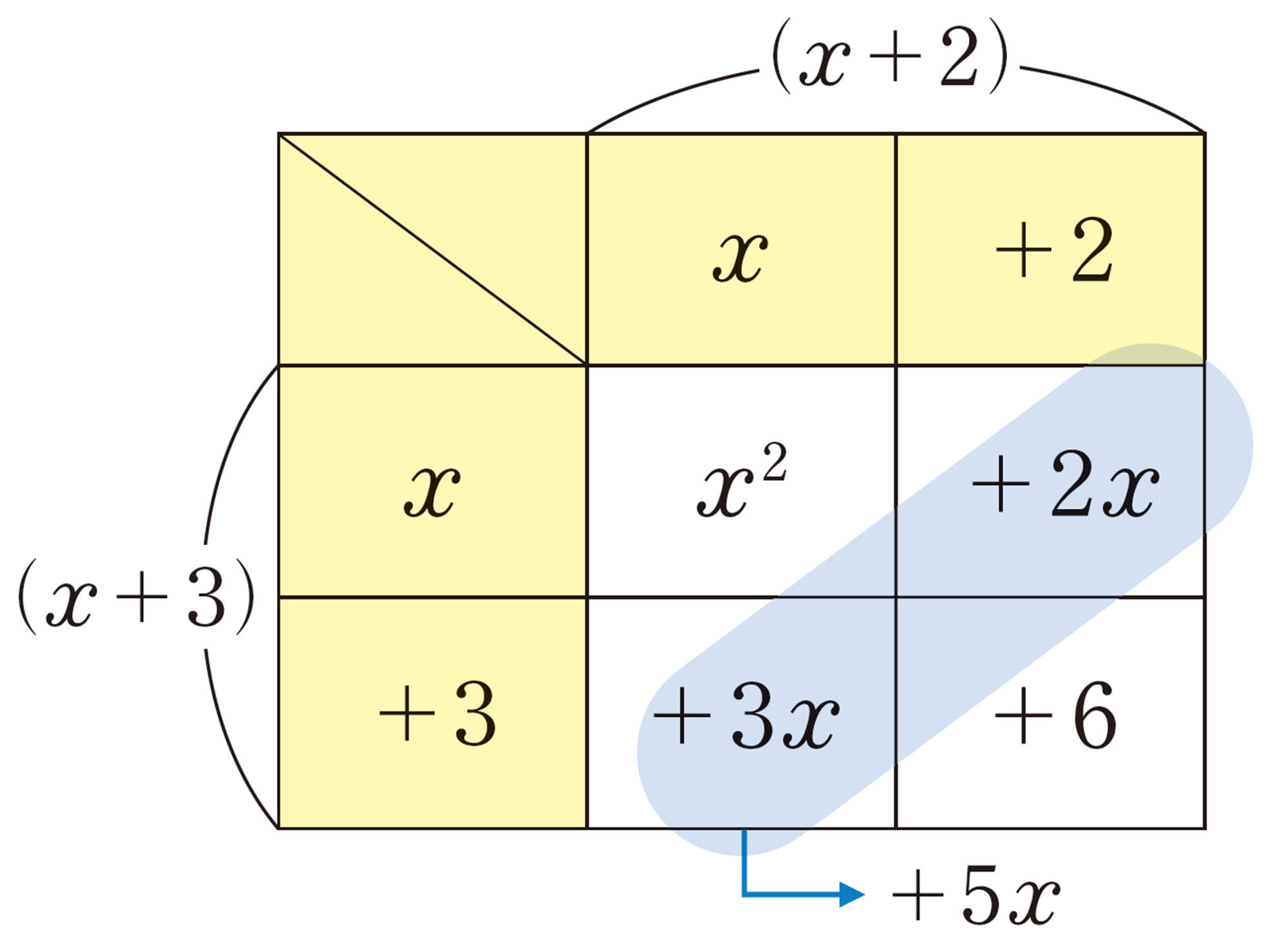
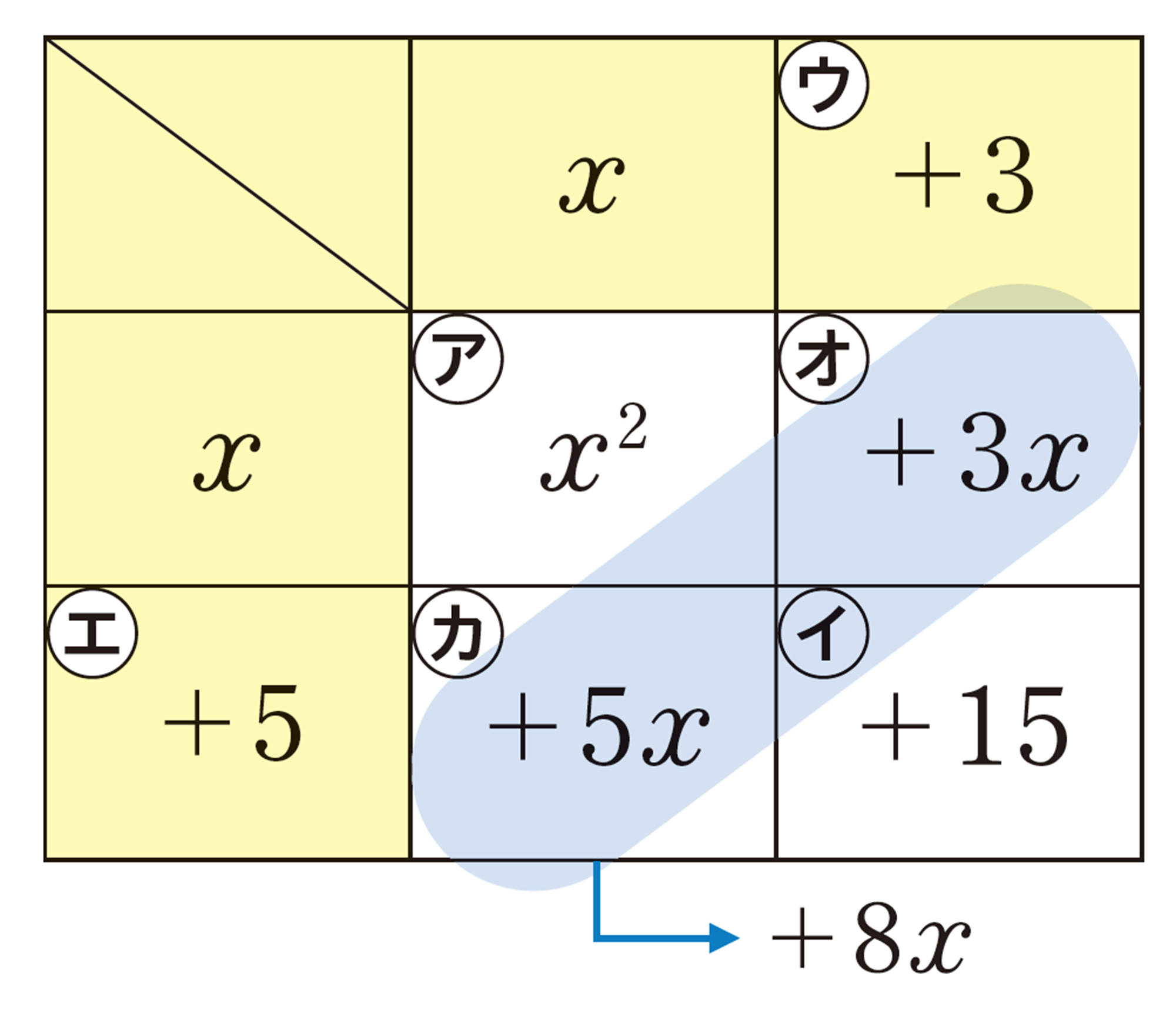
右の表のようにすると,式[mathjax]\((x+2)(x+3)\)を展開することができる。右下の表を使って,[mathjax]\(x²+8x+15\)を因数分解する方法を考えてみよう。
❶ [mathjax]\(x²\)を㋐の欄に,[mathjax]\(+15\)を㋑の欄にそれぞれ記入する。
❷ [mathjax]\(+15\)を,たとえば,[mathjax]\((+3) \times (+5)\)と考えて,[mathjax]\(+3\)を㋒の欄に,[mathjax]\(+5\)を㋓の欄に記入する。
❸ ㋔の欄の[mathjax]\(+3x\)と㋕の欄の[mathjax]\(+5x\)の和が,初めの式の1次の項[mathjax]\(+8x\)と等しいので,次のようになる。
[mathjax]\(x²+8x+15=(x+3)(x+5)\)
<3年p.31>
計算力を高めよう 2
家庭学習や計算練習で利用しましょう。
因数分解 解答 ▷P.300
次の式を因数分解しなさい。
1 共通な因数
⑴ [mathjax]\(xy + 4x\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(5ax – 8ay + 2a\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x² + 7x\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(2x²y – 3xy²\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(6a² + 9ab\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(10x² – 25xy + 5x\)
2 公式による因数分解
⑴ [mathjax]\(x² + 6x + 5\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(x² + 10x + 21\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x² – 7x + 6\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x² – 12x + 27\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(x² + 2x – 8\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(x² – 3x – 10\)
⑺ [mathjax]\(x² – x – 2\)
⑻ [mathjax]\(x² + 4x – 45\)
⑼ [mathjax]\(x² + 14x + 49\)
⑽ [mathjax]\(x² + 16x + 64\)
⑾ [mathjax]\(x² – 10x + 25\)
⑿ [mathjax]\(x² – 20x + 100\)
⒀ [mathjax]\(x² – 1\)
⒁ [mathjax]\(x² – 64\)
3 いろいろな因数分解
⑴ [mathjax]\(4x² + 12x + 9\)
⑵ [mathjax]\(9x² – 6x + 1\)
⑶ [mathjax]\(x² – 2xy + y²\)
⑷ [mathjax]\(x² + 8xy + 16y²\)
⑸ [mathjax]\(100x² – 49\)
⑹ [mathjax]\(16 – 25x²\)
⑺ [mathjax]\(4x² – 49y²\)
⑻ [mathjax]\(x² – \dfrac{y²}{9}\)
⑼ [mathjax]\(ax² – ay²\)
⑽ [mathjax]\(ax² + 2ax + a\)
⑾ [mathjax]\(3x² – 18xy + 27y²\)
⑿ [mathjax]\(2x²y + 4xy – 30y\)
⒀ [mathjax]\(x(x + 3) – 18\)
⒁ [mathjax]\((x – 5)(x – 2) + 2\)
⒂ [mathjax]\((x + 5)(x + 1) + 4\)
⒃ [mathjax]\((x + 1)(x – 4) – 14\)
⒄ [mathjax]\((x – 4)² – 3(x – 4)\)
⒅ [mathjax]\((a – b)x + (a – b)y\)
⒆ [mathjax]\((x + 2)² + (x + 2) – 12\)
⒇ [mathjax]\((x – 5)² – 25\)
(21) [mathjax]\(xy – 5x + y – 5\)
(22) [mathjax]\(2xy – 3x + 2y – 3\)